Automatic lung cancer nodule detection
LUCANODE was the project I developed as part of my master thesis. Based on the LUNA16 dataset, I built a deep learning system to automatically segment and detect cancerous nodules from CT scans.
Abstract
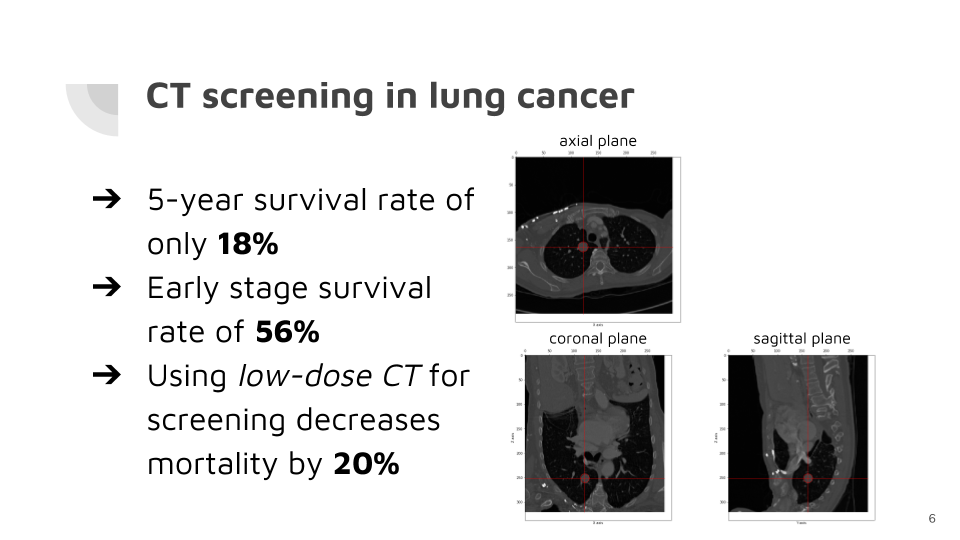
Lung cancer is both the deadliest and one of the most frequently diagnosed forms of the disease. The main cause for the low survivability of lung cancer is due to its lack of early symptoms, which are only detected in terminal stages of the disease. It has been demonstrated that performing screenings in high-risk population increased the survivability by 20% but detecting lung lesions in CT imaging is time consuming and highly dependent on the skill of the radiologist.
lucanode is an open source implementation of a computer-aided detection (CADe) system for lung cancer nodule detection (hence the name) that I developed as part of my Master’s thesis dissertation. Its aim is to provide assistance to radiologists for early diagnosis of lung cancer by detecting round abnormalities in the lung (nodules).
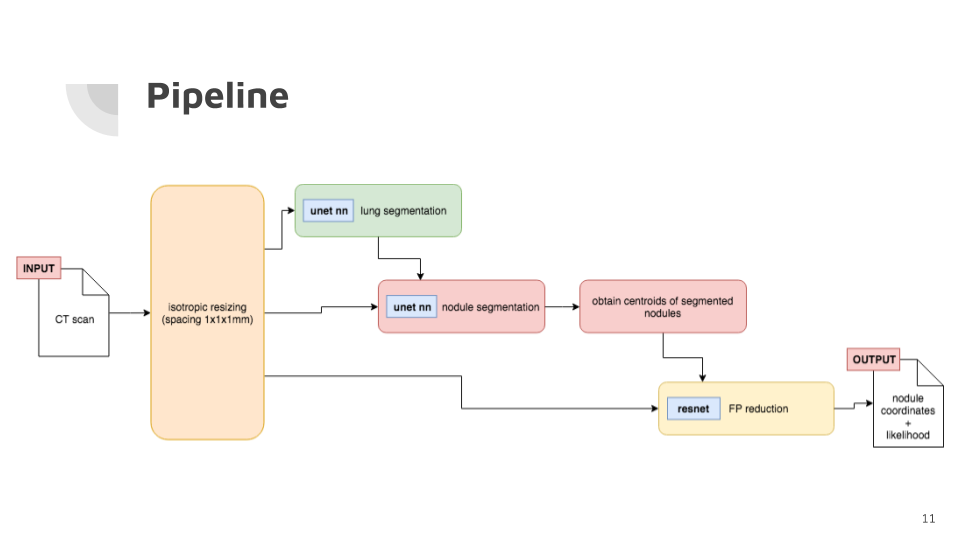
lucanode is divided into a 4 step pipeline:
- scan preprocessing
- lung segmentation
- nodule segmentation
- false positive reduction
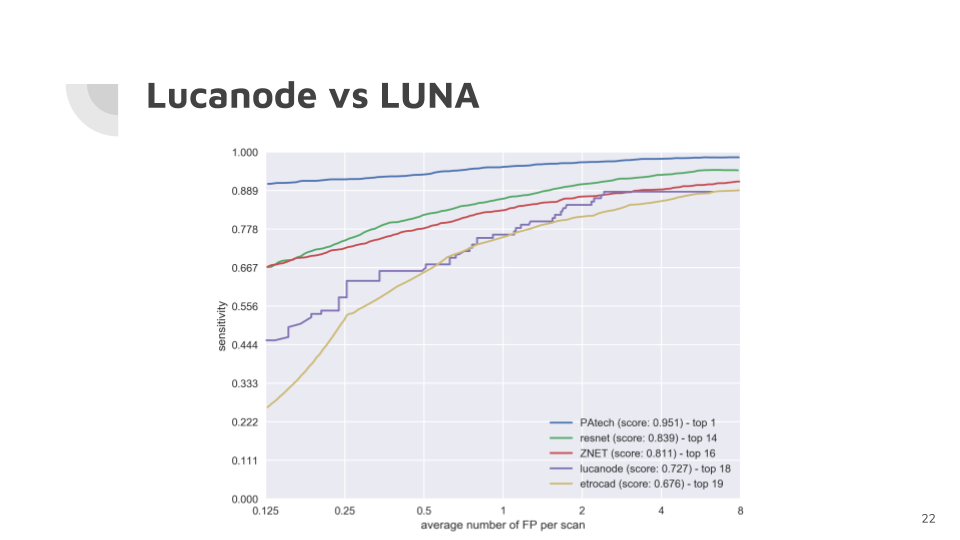
For each step, there are multiple attempted approaches, which have been quantified and evaluated against one another. Finally, the system as a whole is compared against the state of the art following the approach established in the LUNA grand challenge, a public dataset of CT images aimed at detecting lung nodules.
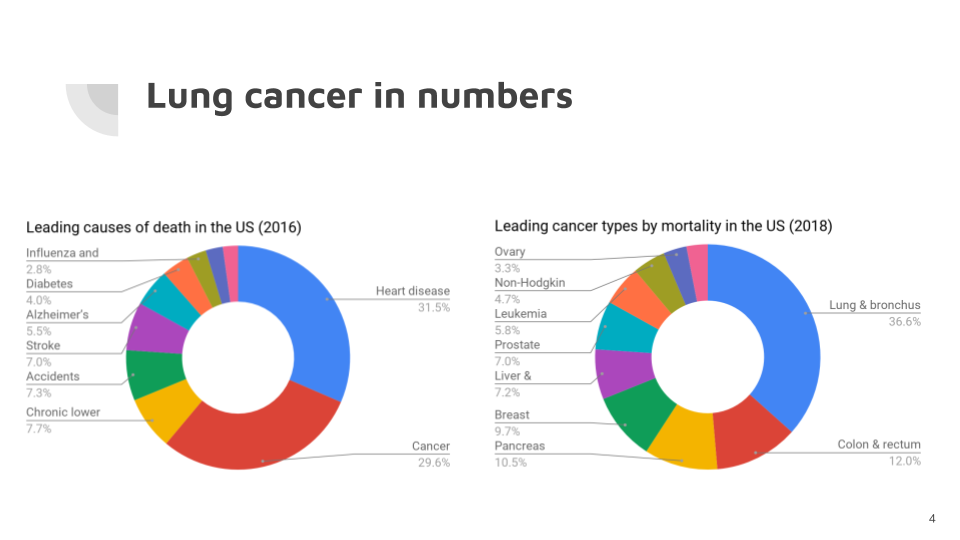
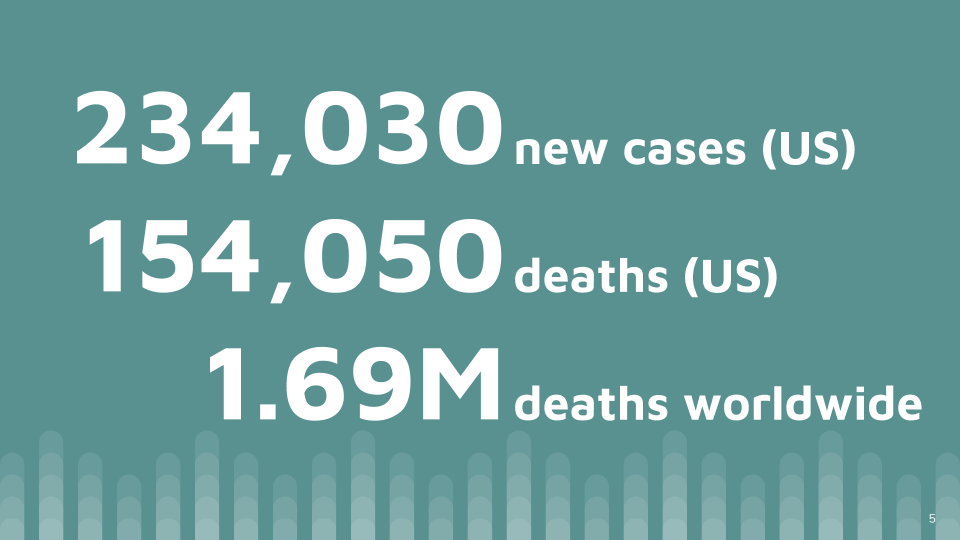
Lung cancer
The pipeline
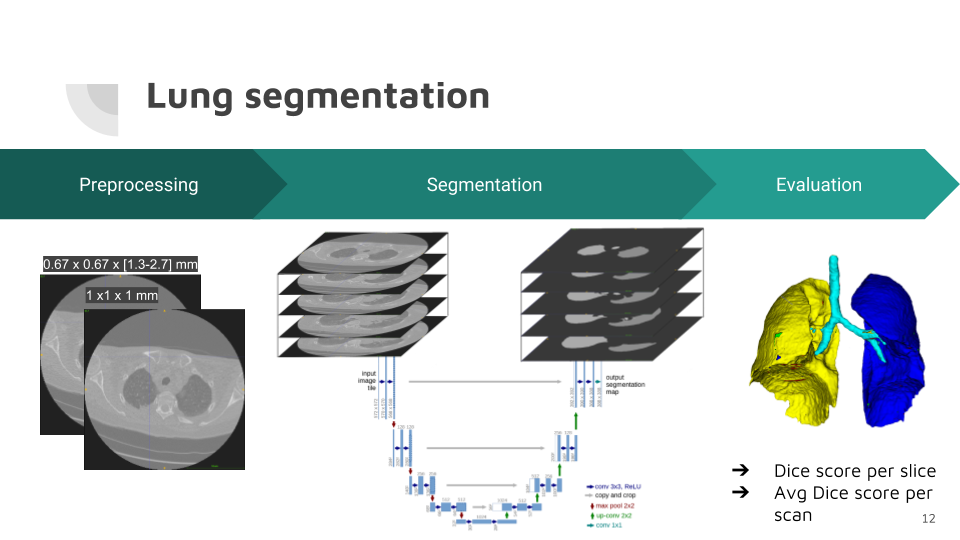
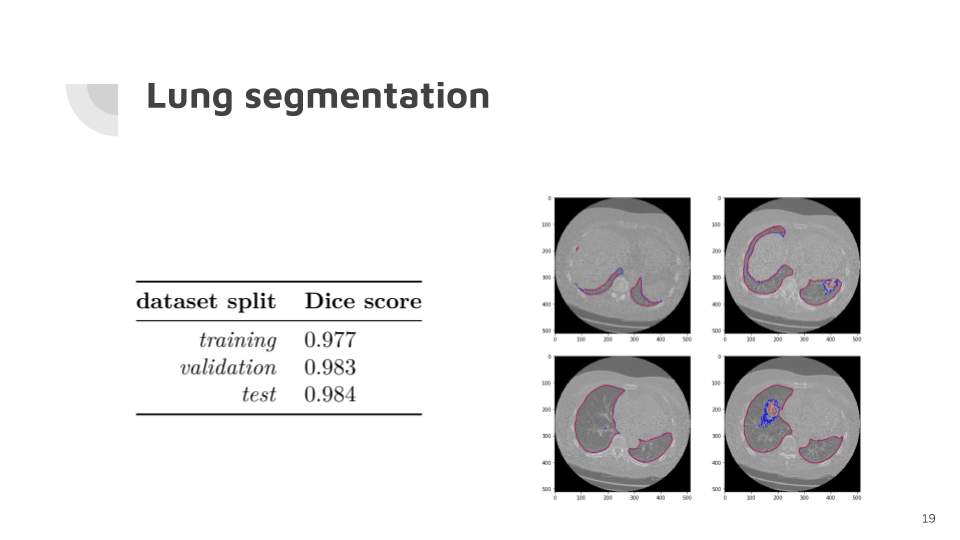
Lung segmentation
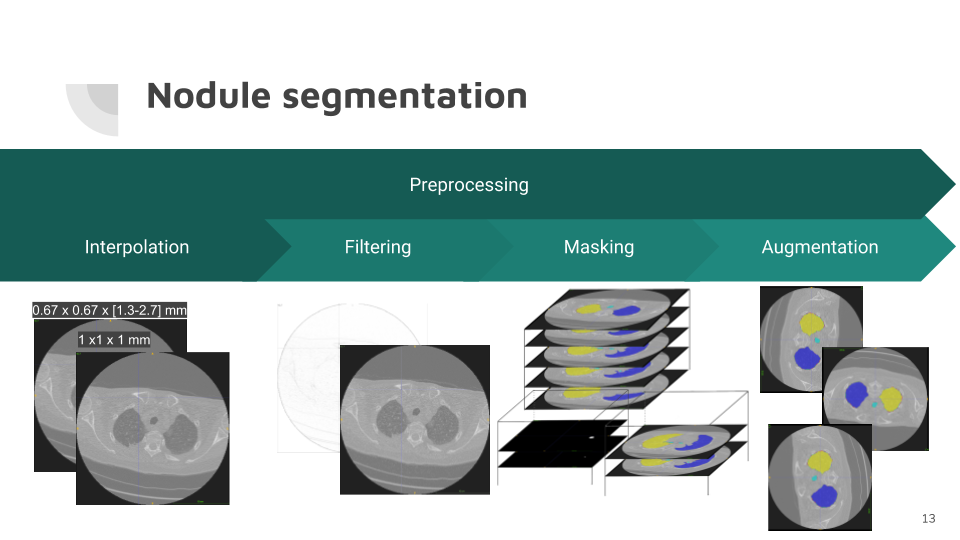
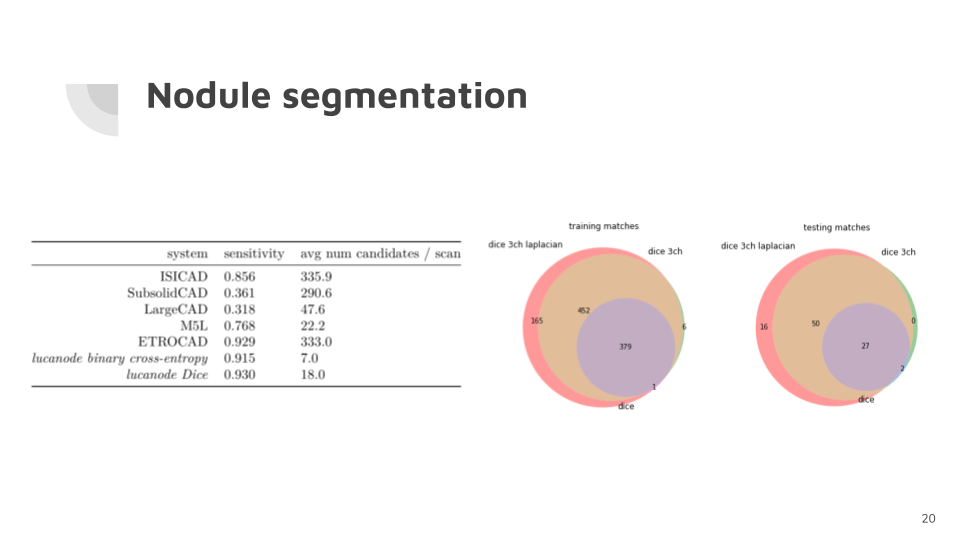
Nodule segmentation
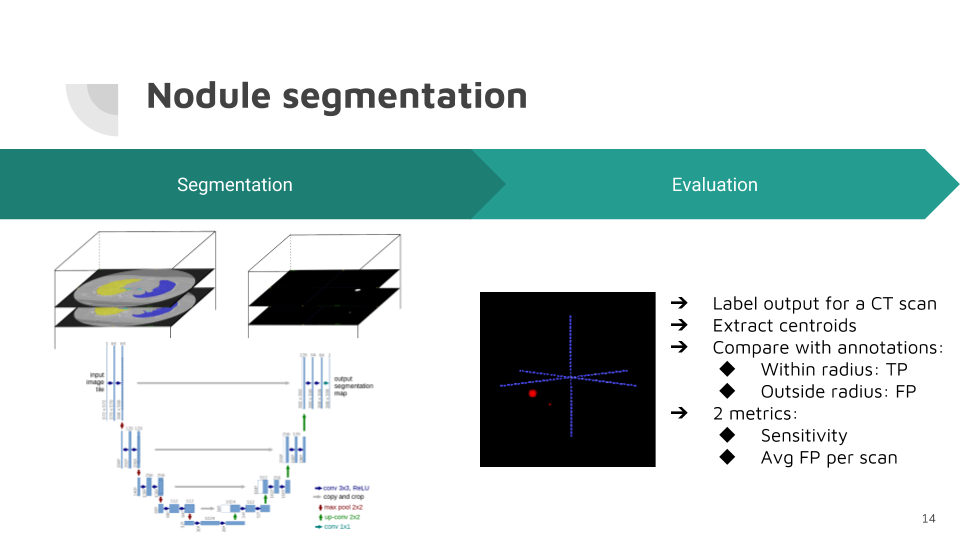
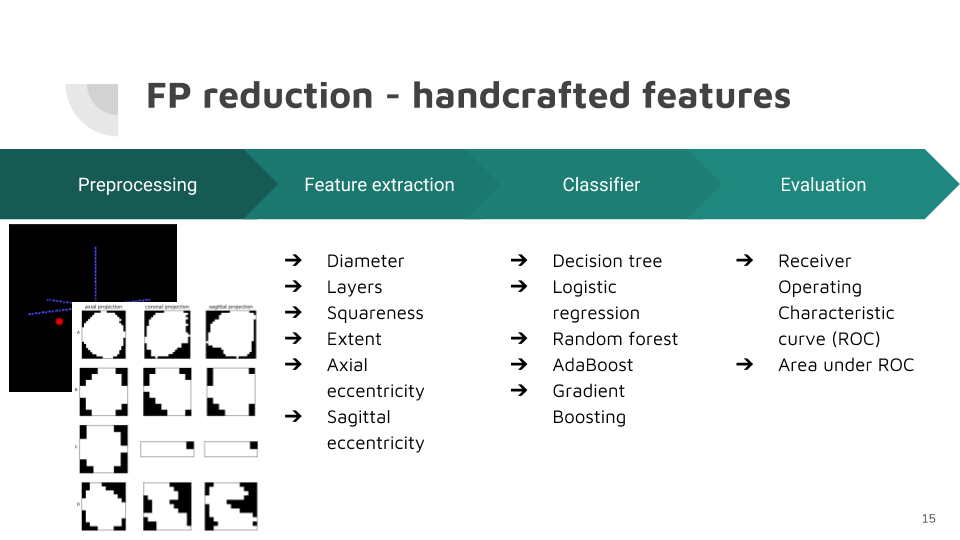
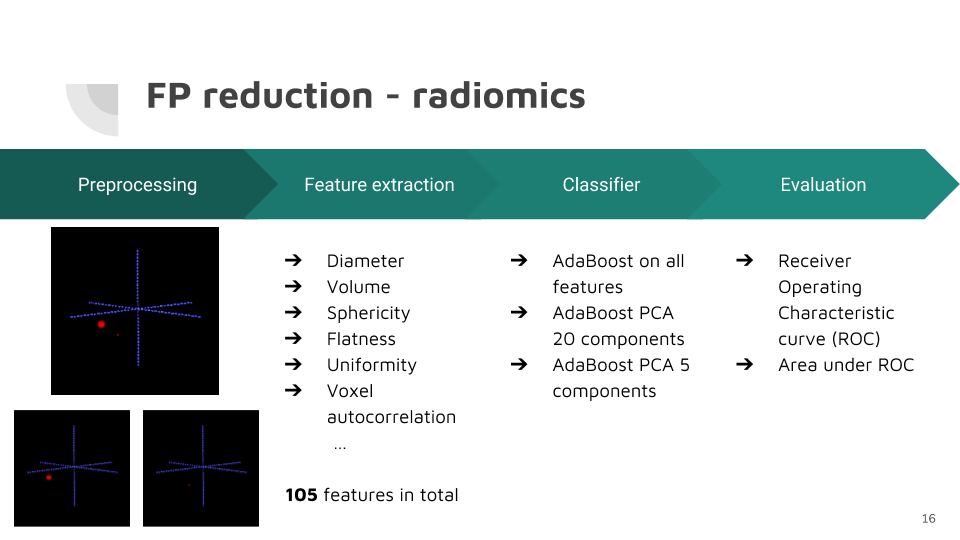
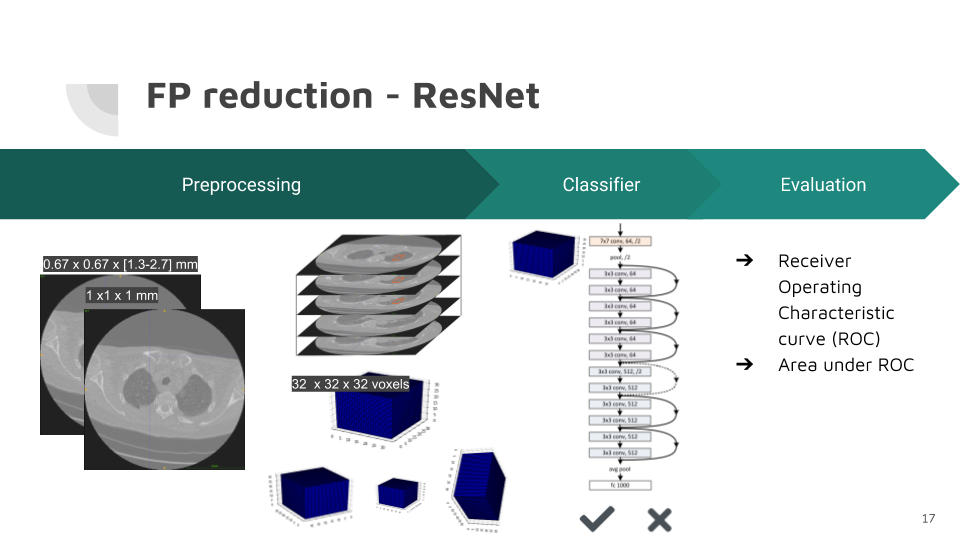
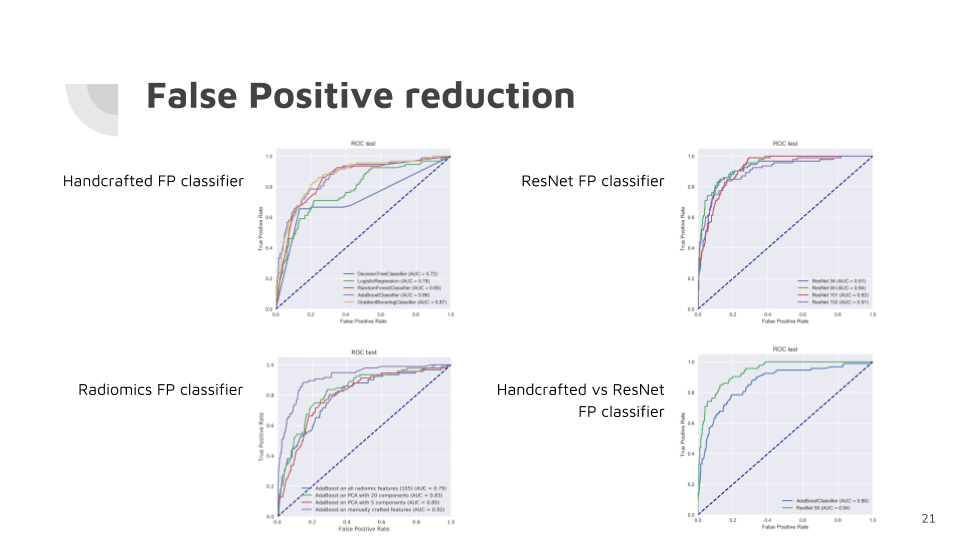
False positive reduction
Results
Available resources
Master thesis pdf.
Source code available on GitHub.
Network weights available on Google Drive.